Project:Spacensus
| Spacensus
| |
|---|---|
| Members | Elliot |
| QR code | |
Part of the London Hackspace graphs and visualisations project.
Overview
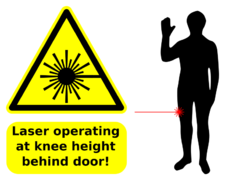
We were donated two Laser Diode Retroreflective Sensors which I now use to monitor space occupancy. The sensors look across the main doorway. The beams are staggered so that direction (arriving, leaving) can be determined by the order in which the beams are broken. They are mounted at waist height.
The sensors are hooked-up to an Arduino via some optocouplers. The Arduino is connected to a PC so that the count can be queried over a network.
The occupancy level is charted on cacti.
Status
Recent modifications
- Milled new bracket for sensors.
- Graphical display with graph showing the days occupancy
- Detection code now completely interrupt driven
- Beams are now polarized
- Beams are now very close together
- Temporary prism reflector being used (permanent replacement on order)
What next
- Fit reflector
- Move sensor closer to door
- Try some different timing configurations to improve detection
- The python script that provides the data to cacti implements only the 'poll for status' command, but will later allow more control and configuration of the counting sensors.
How it works
Sensors
These sensors emit a low power visible laser. They detect the beam reflection - if the reflection is obscured then we can surmise that a person is in the way. The sensors were manufactured in 1996 and use a Class II laser rated at 3mW (peak), 2kHz 2% duty cycle, with a wavelength of 655-670nm (datasheet). The model number is: Q45BB6LL
A good signal can be obtained at 1.5m by using a reflector made of aluminium tape but alignment is critical. Prism reflectors are far more forgiving.
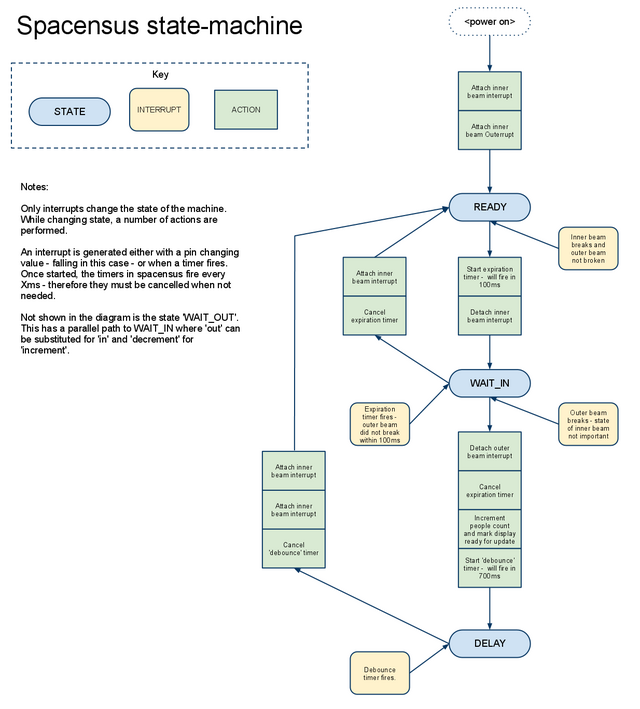
State machine
The detection aspects of spacensus use an interrupt driven state machine. Anything that isn't time critical stuff happens in a run-loop.
Code
The code is available on GitHub - please be kind it's my first Arduino project and I know the code is filth.
Instructions
Changing the count manually
- Press the black increment (+) or decrement (-) buttons on the main unit.
Disabling/Enabling the laser beams
Sometimes you might want to turn off the lasers - perhaps if there are children in the space. Note that no people detection can take place with the lasers off, so please remember to turn them back on.
- If you need to turn off the laser sensors then press and hold both buttons for ~5 seconds
- Repeat above step to enable them.
Silencing the alarm
If the sensors are blocked for more than 15 seconds then an alarm will sound. If you can't remove the blockage you can turn off the sound to prevent irritation.
- Disable the beams as described in the section above.
Powering off
- Remove the USB cable from the side of the unit.
- Remove the 12VDC jack from the side of the unit.
- Check the beams are no longer emitted and that no sensor indicators are illuminated.
Location
The current mounting location has the lasers In close proximity in the middle of the entrance way. To avoid issues with occlusion of beams by coats etc, the coat hooks have been moved to the next wall along, with the lab coats. This arrangement greatly simplifies the detection of the true direction of someone entering/leaving the space. Detection works reasonably well.
Safety signs
FAQ
Q: This will probably get caught out by clusters of people: --81.105.17.61
A:
- We only need an approximate count
- The doorway is narrow so it's unlikely that the steps of more than one individual will overlap.
- Most of the time people won't arrive in clusters
Q: Can we detect some other event such as the door opening after a prolonged lights-out period to force the count to zero? --81.105.17.61
A:
- Yes, using the door/lights data for reset would be good if we get large amounts of drift - but I don't plan to just yet
- This might fail if people spend the night there. AIUI this happens rarely enough that we may not care about the inaccuracy.
- We could also use some kind of probabilistic model with the 'door-open' and 'bell' data
Q: Why didn't you use an ethernet shield?
A: There was already a networked PC in the vicinity.