Project:HackSat One: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (67 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | {{Project||created=10/10/2011|status=Mission Failed|members=[[User:Flux|Flux]], [[User:Datagramm|Samuel]]}} | ||
[[File:Hacksat-devboard-hand.jpeg|thumb|right|Dev board for HackSat One]] | |||
[[File:Radio-testing-at-london-hackspace.jpeg|thumb|right|Radio testing with Samuel]] | |||
HackSat One is a tiny [https://flux.org.uk/projects/hacksat/hardware.html satellite sprite], launching as part of the [http://www.kickstarter.com/projects/zacinaction/kicksat-your-personal-spacecraft-in-space KickSat swarm]. The sprite is powered by its own solar panel and is capable of broadcasting signals back to Earth. It launched on 18th April 2014 as part of a NASA mission to resupply the International Space Station. Due to issues with deployment (see mission update, below) the mission failed. There is a related project to build [[Project:Hackney Space Centre|Hackney Space Centre]]. For the latest information see the [[Mailing List|mailing list]]. | |||
__TOC__ | |||
' | === Mission Update: 14 May 2014 === | ||
I'm sad to report that HackSat will not be stretching its solar panels | |||
after all. HackSat likely re-entered overnight whilst still inside | |||
KickSat. | |||
HackSat launched on 18th April inside the KickSat satellite. KickSat | |||
started out in an orbit of 299 by 331 Kilometers at an inclination of | |||
51.65 degrees. This is a low orbit and subject to a significant amount | |||
of drag. | |||
Sixteen days after launch, KickSat was due to deploy HackSat and its | |||
other satellite sprites. The delay was required by Nasa to avoid | |||
interfering with ISS operations. This meant HackSat would have began | |||
orbiting on 4th May. | |||
On 30th April the watchdog microcontroller that runs the KickSat timer | |||
reset, probably due to a cosmic ray. This pushed the deployment of | |||
HackSat out to 16th May. Attempts to manually deploy HackSat via the | |||
uplink failed: the KickSat batteries never reached a high enough | |||
voltage to enable the uplink receiver. | |||
Since launch signals from KickSat have been regularly received by | |||
ground stations around the world. Recent orbital predictions suggested | |||
that re-entry was likely 13-14th May. No stations have reported | |||
hearing KickSat overnight, so it seems very likely it has already | |||
re-entered. | |||
- [[User:Flux|Flux]] ([[User talk:Flux|talk]]) 09:40, 14 May 2014 (UTC) | |||
== | === Schedule === | ||
After several launch delays, KickSat is now in low Earth orbit. | |||
HackSat and the other sprites will be deploying ~ 20:00 UTC on 4th May. | |||
Our satellite is contained with the bigger KickSat. 128 sprites are loaded into it. It has the names of contributors engraved on it, including "London Hackspace". You can see a [http://zacinaction.github.io/kicksat/engraving_photos/KickSat_minusY_Zoom2.jpg photo of the actual KickSat], complete with our engraving (we're on the bottom row, 4th from the right). | |||
=== Software Payload === | |||
HackSat broadcasts a simple set of data on temperature, magnetic field and angular velocity. It will also broadcast the HackSpace URL: http://hack.rs | |||
If you're interested in trying to receive the signal from HackSat (and | |||
the other KickSat sprites) yourself see [https://github.com/zacinaction/kicksat/wiki/Setting-Up-A-Ground-Station setting up a ground station]. | |||
'' | === Hardware === | ||
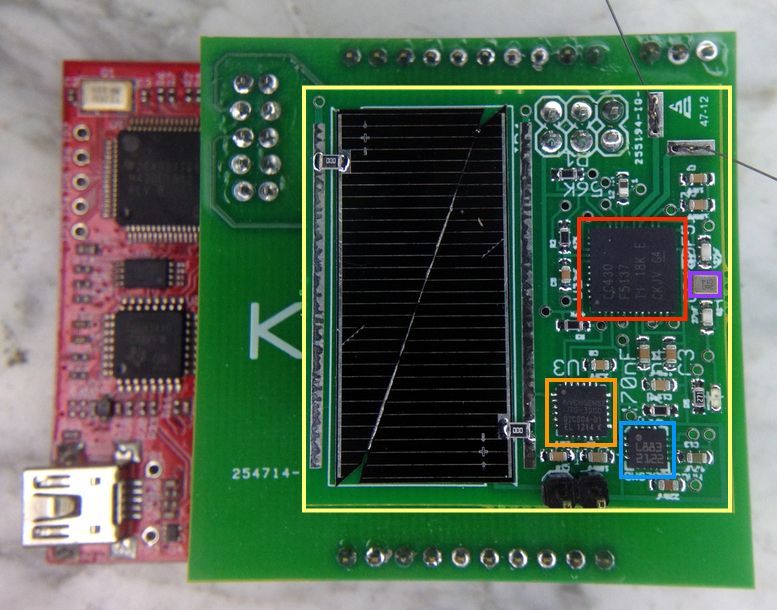
Below, you can see a photograph of the dev board and dev kit. The sprite board itself is outlined in yellow, with the solar panel taking up most of the left-hand side. The boards beneath beneath the sprite are the TI LaunchPad and connecting board. Key components on the spite are: | |||
* '''TI CC430F6137 microcontroller''' (red): 16-Bit [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TI_MSP430 MSP430], 32KB Flash, 4KB RAM, CC1101 Radio [[http://www.ti.com/product/cc430f6137 datasheet]] | |||
* '''InvenSense ITG-3200 Gyroscope''' (orange) [[https://www.sparkfun.com/datasheets/Sensors/Gyro/PS-ITG-3200-00-01.4.pdf datasheet]] | |||
* '''Honeywell HMC5883L Magnetometer''' (blue) [[http://www51.honeywell.com/aero/common/documents/myaerospacecatalog-documents/Defense_Brochures-documents/HMC5883L_3-Axis_Digital_Compass_IC.pdf datasheet]] | |||
* '''TXC 7Z-26.000MDG-T Oscillator''' (purple) [[http://www.txccrystal.com/images/pdf/7z.pdf datasheet]] | |||
* '''Nitinol antennas''' (extend off top right of photograph) [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nitinol nitinol info]] | |||
For more detail on the sprite hardware, including EagleCAD layouts, see the [https://github.com/zacinaction/kicksat/tree/master/Sprite/EagleCAD/Sprite KickSat Git repo]. | |||
''NB. The dev board (pictured) has a different oscillator to that mentioned above.'' | |||
[[File:Annotated-kicksat-dev-board.jpg]] | |||
=== Decal === | |||
[[File:Hacksatone-mission-decal.png]] | |||
''Decal created by Nick Cramp.'' | |||
[[Category:Projects]] | |||
[[Category:Satellites]] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:41, 14 May 2014
| HackSat One | |
|---|---|
| Created | 10/10/2011 |
| Members | Flux, Samuel |
| Project Status | Mission Failed |
| QR code | |
HackSat One is a tiny satellite sprite, launching as part of the KickSat swarm. The sprite is powered by its own solar panel and is capable of broadcasting signals back to Earth. It launched on 18th April 2014 as part of a NASA mission to resupply the International Space Station. Due to issues with deployment (see mission update, below) the mission failed. There is a related project to build Hackney Space Centre. For the latest information see the mailing list.
Mission Update: 14 May 2014
I'm sad to report that HackSat will not be stretching its solar panels after all. HackSat likely re-entered overnight whilst still inside KickSat.
HackSat launched on 18th April inside the KickSat satellite. KickSat started out in an orbit of 299 by 331 Kilometers at an inclination of 51.65 degrees. This is a low orbit and subject to a significant amount of drag.
Sixteen days after launch, KickSat was due to deploy HackSat and its other satellite sprites. The delay was required by Nasa to avoid interfering with ISS operations. This meant HackSat would have began orbiting on 4th May.
On 30th April the watchdog microcontroller that runs the KickSat timer reset, probably due to a cosmic ray. This pushed the deployment of HackSat out to 16th May. Attempts to manually deploy HackSat via the uplink failed: the KickSat batteries never reached a high enough voltage to enable the uplink receiver.
Since launch signals from KickSat have been regularly received by ground stations around the world. Recent orbital predictions suggested that re-entry was likely 13-14th May. No stations have reported hearing KickSat overnight, so it seems very likely it has already re-entered.
- Flux (talk) 09:40, 14 May 2014 (UTC)
Schedule
After several launch delays, KickSat is now in low Earth orbit.
HackSat and the other sprites will be deploying ~ 20:00 UTC on 4th May.
Our satellite is contained with the bigger KickSat. 128 sprites are loaded into it. It has the names of contributors engraved on it, including "London Hackspace". You can see a photo of the actual KickSat, complete with our engraving (we're on the bottom row, 4th from the right).
Software Payload
HackSat broadcasts a simple set of data on temperature, magnetic field and angular velocity. It will also broadcast the HackSpace URL: http://hack.rs
If you're interested in trying to receive the signal from HackSat (and the other KickSat sprites) yourself see setting up a ground station.
Hardware
Below, you can see a photograph of the dev board and dev kit. The sprite board itself is outlined in yellow, with the solar panel taking up most of the left-hand side. The boards beneath beneath the sprite are the TI LaunchPad and connecting board. Key components on the spite are:
- TI CC430F6137 microcontroller (red): 16-Bit MSP430, 32KB Flash, 4KB RAM, CC1101 Radio [datasheet]
- InvenSense ITG-3200 Gyroscope (orange) [datasheet]
- Honeywell HMC5883L Magnetometer (blue) [datasheet]
- TXC 7Z-26.000MDG-T Oscillator (purple) [datasheet]
- Nitinol antennas (extend off top right of photograph) [nitinol info]
For more detail on the sprite hardware, including EagleCAD layouts, see the KickSat Git repo.
NB. The dev board (pictured) has a different oscillator to that mentioned above.
Decal
Decal created by Nick Cramp.